Can you use a leaf blower with eusphatian tube dysfunction Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a condition that affects the small passageways connecting the middle ear to the throat. These tubes play a vital role in balancing air pressure and draining fluid from the ears. However, individuals with ETD often face challenges when exposed to high noise levels or vibrations, as these factors can worsen symptoms and lead to significant discomfort or complications.
For those who depend on power tools like leaf blowers for outdoor tasks, the question arises: Is it safe to use a leaf blower if you have ETD? This article explores the potential risks associated with leaf blowers and their impact on ETD. It also provides practical tips to help you protect your ears while maintaining efficiency, whether you’re a homeowner or a professional landscaper managing this condition.
By understanding the connection between noise, vibrations, and ETD, you can make informed decisions to minimize harm while effectively handling your outdoor maintenance needs.
Understanding can you use a leaf blower with eusphatian tube dysfunction
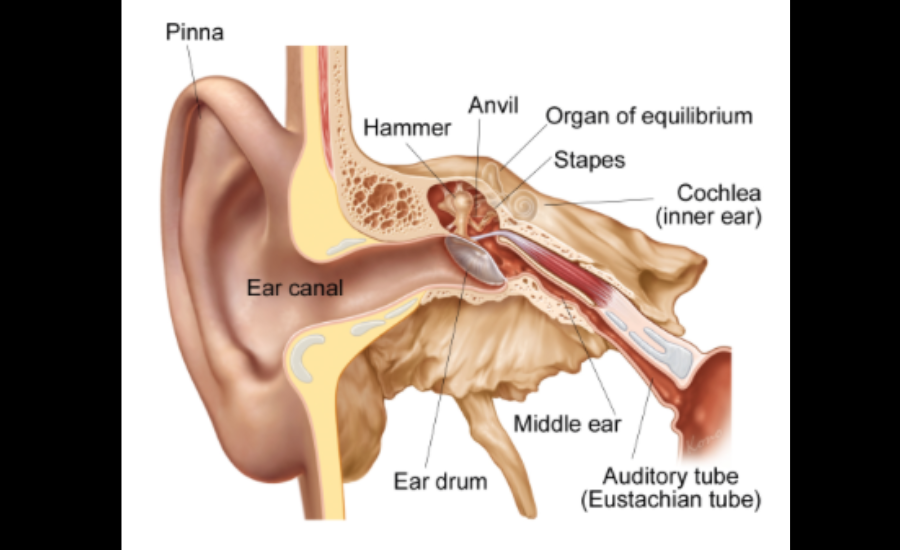
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) occurs when the tubes connecting the middle ear to the throat fail to open or close as they should. This dysfunction can lead to symptoms such as ear pain, pressure imbalances, and muffled hearing. Common causes include allergies, infections, or structural abnormalities, while environmental factors like loud noises and vibrations often intensify the condition.
Leaf blowers are known to produce noise levels exceeding 85 decibels (dB), a threshold linked to potential hearing damage. For individuals with ETD, exposure to such intense noise can strain the already sensitive mechanisms of the Eustachian tubes. Additionally, the vibrations generated by operating machinery like leaf blowers may aggravate discomfort and worsen existing symptoms, making it essential to approach their use with caution.
Risks of Using Leaf Blowers with ETD
For those managing Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD), operating a leaf blower without proper precautions can introduce several challenges:
Noise-Related Strain
The high-frequency sound of a leaf blower can disrupt the delicate balance of the Eustachian tubes, leading to increased ear pain, a sensation of fullness, and a worsening of symptoms. These fluctuations in pressure caused by loud noise can be particularly problematic for individuals with ETD.
Impact of Vibrations
Leaf blowers generate significant vibrations that can travel through the body, potentially irritating the inner ear. This mechanical stress may interfere with how the Eustachian tubes regulate pressure, further aggravating the condition.
Higher Infection and Fluid Retention Risks
Extended exposure to loud noises can strain the middle ear, increasing the likelihood of infections. Since ETD already impairs fluid drainage, the added stress from improper use of a leaf blower can heighten the risk of complications, including fluid build-up or inflammation.
Safe Leaf Blower Use for Those with ETD
Managing Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) doesn’t mean you must avoid leaf blowers entirely. By adopting specific precautions, you can reduce risks while completing outdoor tasks effectively.
Wear Hearing Protection
Invest in high-quality earplugs or noise-canceling earmuffs designed to block harmful noise levels. Industrial-grade hearing protection can shield your ears from the loud sounds generated by leaf blowers, helping to prevent further irritation.
Choose Quieter Models
Modern leaf blowers are available with quieter engines, particularly battery-powered models, which typically produce less noise than gas-powered alternatives. Opting for a low-decibel machine can significantly reduce the strain on your ears.
Use Anti-Vibration Gear
Anti-vibration gloves are designed to absorb mechanical shocks, minimizing the vibrations that travel through your hands and potentially affect your ears. These gloves are a valuable addition when using power tools.
Limit Usage Time
Break your work into shorter sessions, allowing time between tasks for your ears to recover. Limiting prolonged exposure to noise and vibration can help reduce the impact on your Eustachian tubes.
Practice Proper Technique
Maintain an upright posture while using the leaf blower to avoid unnecessary strain on your body. Proper handling not only improves efficiency but also lessens the effects of vibrations on your ears and overall health.
Alternatives to Leaf Blowers for ETD Management
If you’re concerned about the potential impact of leaf blowers on your ear health, there are effective alternatives to keep your yard tidy without risking your Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) symptoms.
Raking
Raking is a manual, noise-free solution that eliminates exposure to harmful noise and vibrations. While it requires more physical effort, it’s a safe and practical choice for maintaining small to medium-sized yards.
Electric Sweepers
Electric sweepers offer a quieter and less vibration-intensive alternative to traditional leaf blowers. These tools provide a balanced option for those who prefer mechanical assistance without the same level of noise exposure.
Professional Landscaping Services
For individuals with severe or persistent ETD, hiring a professional landscaping service is a stress-free solution. This approach removes the need for direct exposure to potential triggers, ensuring your yard is maintained without compromising your ear health.
How Leaf Blowers Affect Individuals with ETD
Pressure Fluctuations
For those with Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD), even minor changes in air pressure can result in significant discomfort. The bursts of air generated by a leaf blower can travel to the ears, exacerbating symptoms. These pressure imbalances may cause pain, dizziness, or worsened hearing, making it crucial to consider the impact of such tools on sensitive ears.
Noise Sensitivity
Leaf blowers are notoriously loud, often producing noise levels that can heighten discomfort for individuals with ETD. Dysfunctional Eustachian tubes struggle to regulate middle ear pressure effectively, making the ears more sensitive to sound pressure changes. Extended exposure to loud noise can also lead to additional complications, such as tinnitus or hearing damage.
Exposure to Allergens and Irritants
Leaf blowers stir up dust, pollen, and other particulates, which can aggravate allergies and sinus issues—common triggers for ETD. Inhaling these airborne irritants may lead to nasal congestion, further blocking the Eustachian tubes and intensifying symptoms.
Precautions for Using a Leaf Blower with ETD
If you have Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) and still choose to use a leaf blower, taking careful steps can help reduce potential risks and discomfort.
Protect Your Hearing
Wearing proper hearing protection, such as foam earplugs or noise-reducing earmuffs, can significantly lower your exposure to harmful noise levels. Ensure the protection fits securely and is rated to block high decibels effectively. However, consult a healthcare professional before using earplugs, as they may sometimes worsen pressure issues for individuals with ETD.
Choose a Quieter Option
Switching to an electric-powered leaf blower with lower noise output can be beneficial. These quieter models produce less sound pressure, reducing the likelihood of triggering ETD symptoms while still being effective for yard work.
Minimize Allergen Exposure
If allergens worsen your ETD, wear a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) mask while operating the leaf blower. This can filter out small particles like dust and pollen, helping to prevent nasal congestion and reducing the risk of exacerbating ETD symptoms.
Consider Manual Alternatives
For those highly sensitive to noise or pressure, manual tools like rakes or brooms offer a safe alternative. Although more time-consuming, these methods eliminate the risks associated with air pressure changes and loud noise.
Take Regular Breaks
Frequent breaks during yard work can help alleviate pressure buildup in the ears. If you experience discomfort, stop immediately and allow time for recovery. Simple actions like swallowing, yawning, or staying hydrated can also help relieve ear pressure and improve comfort.
Also Read: Vicki Naas Frederick MD
Final Words
Using a leaf blower with Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is possible, but it requires careful precautions to avoid worsening symptoms. ETD affects the tubes that regulate ear pressure, making loud noises, vibrations, and allergens potential triggers for discomfort. Opt for quieter, electric-powered leaf blowers to reduce noise exposure, and wear noise-canceling ear protection to shield your ears. Anti-vibration gloves can help minimize mechanical stress, while HEPA masks filter out allergens that may exacerbate ETD symptoms. Consider breaking tasks into shorter sessions to allow your ears to recover. For those highly sensitive to noise or pressure, manual tools like rakes or electric sweepers are safer alternatives.
FAQs
1. Is it safe to use a leaf blower if I have Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD)?
Using a leaf blower with ETD is possible, but it requires extra precautions. The noise and vibrations from the blower can worsen symptoms, causing ear pain, pressure imbalances, and discomfort. It’s important to protect your ears by using hearing protection, choosing quieter models, and limiting exposure time.
2. How does noise from a leaf blower affect my ETD?
Loud noises, such as those produced by a leaf blower, can exacerbate the symptoms of ETD. The pressure fluctuations caused by high-decibel sounds can disrupt the function of the Eustachian tubes, leading to increased ear pain and discomfort.
3. What can I do to protect my ears when using a leaf blower with ETD?
To protect your ears, wear high-quality hearing protection such as foam earplugs or noise-reducing earmuffs. You can also opt for quieter, electric-powered leaf blowers and use anti-vibration gloves to reduce mechanical stress on your body and ears.
4. Are there quieter alternatives to leaf blowers for people with ETD?
Yes, there are quieter alternatives such as electric sweepers and manual rakes. These options produce less noise and vibration, making them safer for individuals with ETD. Hiring a professional landscaping service is another option to avoid direct exposure to potential triggers.
5. Can I still use a leaf blower if I have ETD and allergies?
If you have both ETD and allergies, the use of a leaf blower may aggravate your symptoms due to the dust and allergens it stirs up. Wearing a HEPA mask while operating the blower can help reduce allergen exposure, and using a quieter model will minimize noise-related discomfort.
6. How can I minimize the risk of fluid buildup in my ears while using a leaf blower with ETD?
To minimize the risk of fluid buildup, limit the amount of time you spend using the leaf blower, take frequent breaks, and practice techniques like swallowing or yawning to help relieve ear pressure. Wearing ear protection and using anti-vibration gear can also reduce strain on the ears.
7. What should I do if I experience discomfort while using a leaf blower with ETD?
If you experience discomfort, stop using the leaf blower immediately and take a break. Try to relieve ear pressure by yawning, swallowing, or staying hydrated. If the discomfort persists, consult a healthcare professional for further advice.
8. Are there any risks of using a leaf blower with ETD in the long term?
Extended use of a leaf blower without proper precautions can lead to long-term issues such as increased ear pain, pressure imbalances, and potential hearing damage. It’s crucial to take steps to protect your ears, limit exposure time, and consider alternative methods if necessary.
9. Can I use a leaf blower for short periods with ETD?
Yes, short periods of leaf blower use can be manageable for individuals with ETD, as long as you take breaks and use proper ear protection. Limiting exposure time and monitoring your symptoms can help prevent discomfort and complications.
10. What is the best type of leaf blower for someone with ETD?
The best type of leaf blower for someone with ETD is a quieter, electric-powered model. These produce less noise and vibration compared to gas-powered models, reducing the strain on your ears and minimizing the risk of exacerbating ETD symptoms.
For exclusive insights and expert tips, stay connected with Creative Insider.